language variety in sociolinguistics, pidgin and creole definition, difference between creole and pidgin, pidgin and creole examples, difference between register and dialect, dialect and register definition, types of dialect and register, dialect and register examples, Try.Fulfil
 |
| Pidgin and Creole, Dialect and Register, Variety of language, try.fulfil |
Dialect
and Register:
Dialect and register are the two major varieties
of language in sociolinguistics. If we judge language as a fact which
includes all languages of the world, then `language variety in
sociolinguistics’ will come in the table of discussion. In the field of ‘varieties
of language’ a single language variety must be different from another
variety of language as it possesses separate linguistic features. But it
doesn’t seem that there won’t be any relation between two language varieties.
Now, have a look on the two varieties of language in sociolinguistics
`Register and Dialect’. Also we’ll try to seek the difference between `dialect
and register’ as well as the similarities between the two varieties `Register
and Dialect’.
Read More : Varieties of Sociolinguistics.
> Linguistics Bangla Lectures..
Definition of Dialect and Register:
Dialect Definition:
The variety of language `Dialect’ stands for a subset
of language that is spoken in a part of a country or spoken by a specific
social class. This language variety has some differences in vocabulary, pronunciation
and some differences in grammar. Dialect is a variety of language based
on users and has a specific accent. Several dialects may emerge in a particular
language. But all dialects of a language have same dignity. Sometimes, a
particular dialects gets much importance and becomes `Standard Language’. If
there is a question – what are the examples of dialect? Answer will be –
the examples of dialect are `Sylheti dialect, Chittagong’s dialect,
Dhaka’s dialect’. (Located in Bangladesh).
Register Definition:
Register is a significant variety of language used by
a single group of people normally who are from the same profession. It is a
special form of a language used in special situation. If someone asks – what
are the examples of register? Answer will be like that – the examples
of register are `the speaking system of Doctors or Lawyers, Businessmen or
Engineers.
Types of Dialect and Register:
Types of
Dialect:
To have the classification of dialect; there are two types
of dialect are available. The first one is social dialect and the
second one is regional dialect. Let’s have a look on the two types of
dialect.
Social
Dialect / Sociolect:
The language variety Sociolect or social dialect is a
subset of language spoken by a specific community. Sociolect has its own
accent, grammar and vocabulary. An example of sociolect or social dialect
is the language of lower class and of higher class people of society.
Regional
Dialect:
It is a variety of language which is spoken by the
people of a specific area or region. It also has distinctive accent with
vocabulary and grammar. An example of regional dialect is the dialect of
Sylhet or Chittagong of Bangladesh.
Types of Register:
Halliday defines three types of register / (classification
of register).
1. Field – It is concerned about the subject and purpose.
2. Mode – It traces the way of communication.
3. Tenor- It deals with the relations of participants.
Difference between Dialect and Register:
|
Dialect ( Edited by Try.Fulfil) |
Register
( Written by Saiful Munna) |
|
1. A variety of language spoken by specific social
class. 2. It’s the variety of language spoken in a
specific region. 3. Dialect has distinct pronunciation, vocabulary and
grammar. 4. It has specific accent. 5. A particular dialect may become Standard Language. 6. Dialect is used in all situations. 7. Examples of dialect are Sylheti dialect,
Chittagong’s dialect, Dhaka’s dialect. 8. Dialect has two types. 1. Sociolect. 2. Regional
dialect. |
1. Register is the variety of language spoken by
group of people of the same profession. 2. It is spoken in different region by same professionals. 3. Register has specific vocabulary and speaking style but
doesn’t have distinct grammar. 4. It doesn’t have specific accent. 5. Register can’t become a Standard Language. 6. It is used in special situation. 7. Examples of register are the language used by
Doctors, Businessmen or Lawyer etc. 8. Halliday defines three types of register. Try.Fulfil |
Pidgin
and Creole:
To speak about language variety in linguistics,
pidgin and creole are the two prominent varieties of sociolinguistics. These
two varieties of language are much close to the main language. Pidgin emerges
from contacts between different language speakers and creole is the result of a
pidgin while it becomes native language.
Q- Define pidgin and creole.
Pidgin and Creole definition:
Pidgin definition:
It is assumed that the word `pidgin’ had created by the
Chinese while they uttered the word “business” as ‘bigeon’. Later this ‘bigeon’
changed to ‘bidgin’ and further ‘pidgin’. To trance the definition of pidgin,
when different language speakers come close and have need to communicate with
each other but they don’t have a common language; they make a new language
gathering vocabulary and features of their separate languages, it is called
pidgin.
As pidgin is mostly needed and used in business purpose, it
is also called “Trade Language”. Sometimes pidgin is also used as ‘lingua
franca’.
Creole definition:
The variety of language ‘pidgin’ may be stable
for long and it will be the first language for the descendants of the pidgin
speakers. So, when a pidgin is used as first language and gets the status of
mother tongue of a community, it is called Creole. A pidgin turns into a creole
by the passage of time. Examples of creole are Jamaic Creole, Dominica Creole.
Another example is Haiti Creole.
Difference between Creole and Pidgin:
Though the two varieties of sociolinguistics are
closely related to each other, pidgin and creole have some differences.
Let’s have a look on the difference between pidgin and creole.
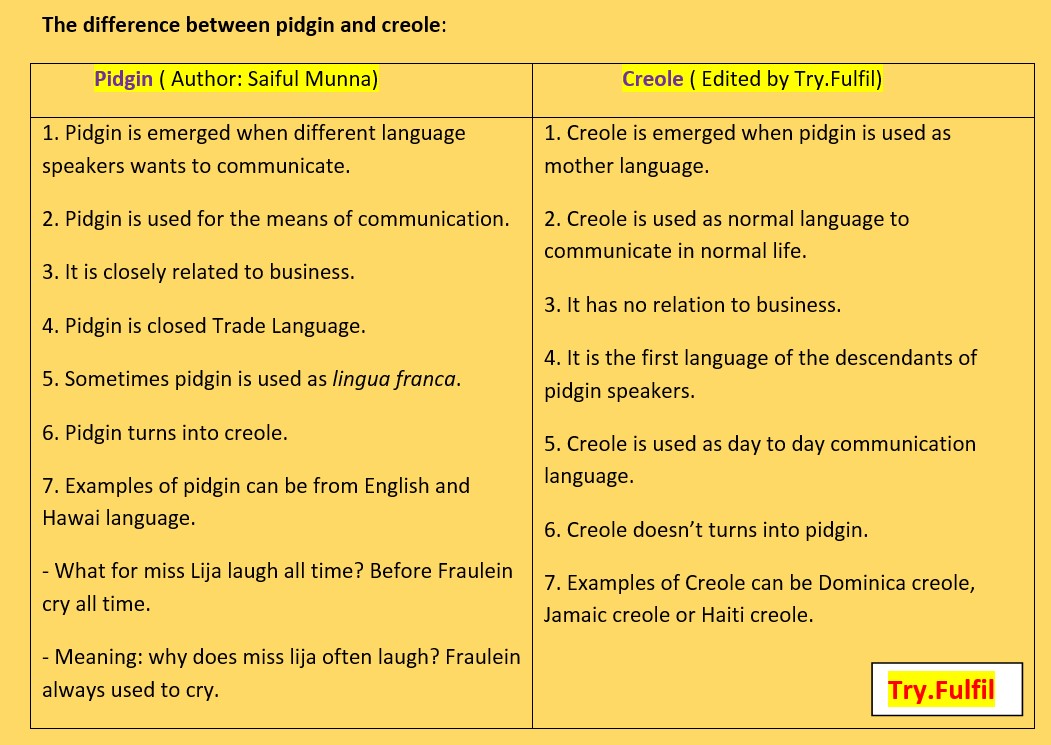
The difference between pidgin and creole:
|
Pidgin ( Author: Saiful Munna) |
Creole ( Edited by Try.Fulfil) |
|
1. Pidgin is emerged when different language speakers
wants to communicate. 2. Pidgin is used for the means of communication. 3. It is closely related to business. 4. Pidgin is closed Trade Language. 5. Sometimes pidgin is used as lingua franca. 6. Pidgin turns into creole. 7. Examples of pidgin can be from English and Hawai
language. - What for miss Lija laugh all time? Before Fraulein cry
all time. - Meaning: why does miss lija often laugh? Fraulein always
used to cry. |
1. Creole is emerged when pidgin is used as mother
language. 2. Creole is used as normal language to communicate in
normal life. 3. It has no relation to business. 4. It is the first language of the descendants of pidgin
speakers. 5. Creole is used as day to day communication language. 6. Creole doesn’t turns into pidgin. 7.
Examples of Creole can be Dominica creole, Jamaic creole or Haiti
creole. Try.Fulfil |
 |
| Difference between dialect and register, register and dialect difference , try.fulfil |
For downloading the image of the difference between Pidgin and Creole, see this image.
 |
| Difference of creole and pidgin, difference between pidgin and creole, try.fulfil |
















0 Comments