What is Morphology? What is Morpheme? Classify the morphemes in detail. (NU '14,16,18)
( Short points: Morpheme, Morphology, Classes of Morpheme, Free Morpheme, Lexical Morpheme, Content Morpheme, Referential Morpheme, Grammatical Morpheme, Functional Morpheme, Bound Morpheme, Inflectional Morpheme, Derivational Morpheme.)
 |
| Classification of morphemes with diagram | Major classes of morpheme. |
Answer:
Morpheme is the smallest meaningful unit of a word or language. Morpheme is that part of a word which can't be broken.
For example:
nation
nation +al
nation +al +iz
nation +al+ iz+ ation
All the unbroken parts of this word are morphemes. As follows: nation, al, iz, ation.
In defining morphology, the level of linguistics which studies the smallest meaningful units of a language, their several forms and the rules by which words are constructed is known as morphology.
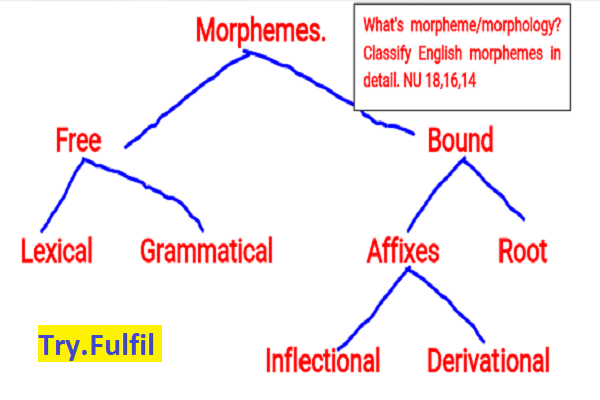
Major classes of morphemes are two.
1. Free Morpheme. 2. Bound Morpheme.
They can also be divided into several parts as free morpheme to Lexical and Grammatical Morpheme. Furthermore, bound morpheme to Affixes and Root. Affixes are divided into Inflectional and Derivational Affixes. This classification is drawn as follows:
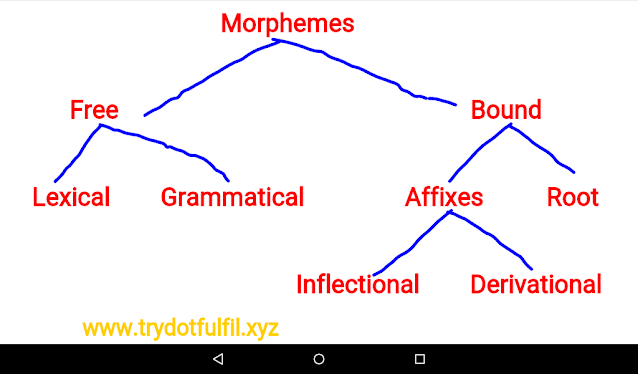 |
| Classification of morphemes diagram |
Free Morpheme:
The morpheme that can stand alone as an independent word is called free morpheme. Such as: boy, doll, is, are, nation, morpheme. It can be segmented as : Lexical Morpheme and Grammatical Morpheme.
Lexical / Content / Referential Morpheme:
Lexical Morpheme or Content Morpheme has a more specific meaning and large in number. It is classified as noun, verb, adjective a d adverb.
Grammatical / Functional Morpheme: Grammatical morpheme or functional morpheme has less specific meaning, limited in number and explains grammatical relationships. It is classified as articles, prepositions, auxiliary verbs etc.
Bound Morpheme:
The morpheme that can't stand alone as an independent word and needs the help of a free morpheme is called bound morpheme. e.g. al of national.
Bound morpheme has two sorts, Affixes and Root. Affixes are of two sorts: Inflectional Morpheme and Derivational Morpheme.
Inflectional Morpheme:
Inflectional Morpheme serves a pure grammatical function and doesn't change the meaning of a word.
i.e.. number, person, gender, case etc.
In more specific, 's' of the word "runs".
Derivational Morpheme:
Derivational Morpheme is an affix which is added to a word and creates a new word. It is of two classes: Class maintaining and class changing.
e.g. un+ happy = unhappy.

















0 Comments